ANALISIS VARIASI SUHU DAN ARUS PADA ELEKTROPLATING CU DENGAN ANODA AL PADA LARUTAN NI DAN AGNO₃ MENGGUNAKAN METODE POTENSIOSTATIK
Keywords:
Electroplating, Potentiostatic, Deposition , Conductivity, ElectrolyteAbstract
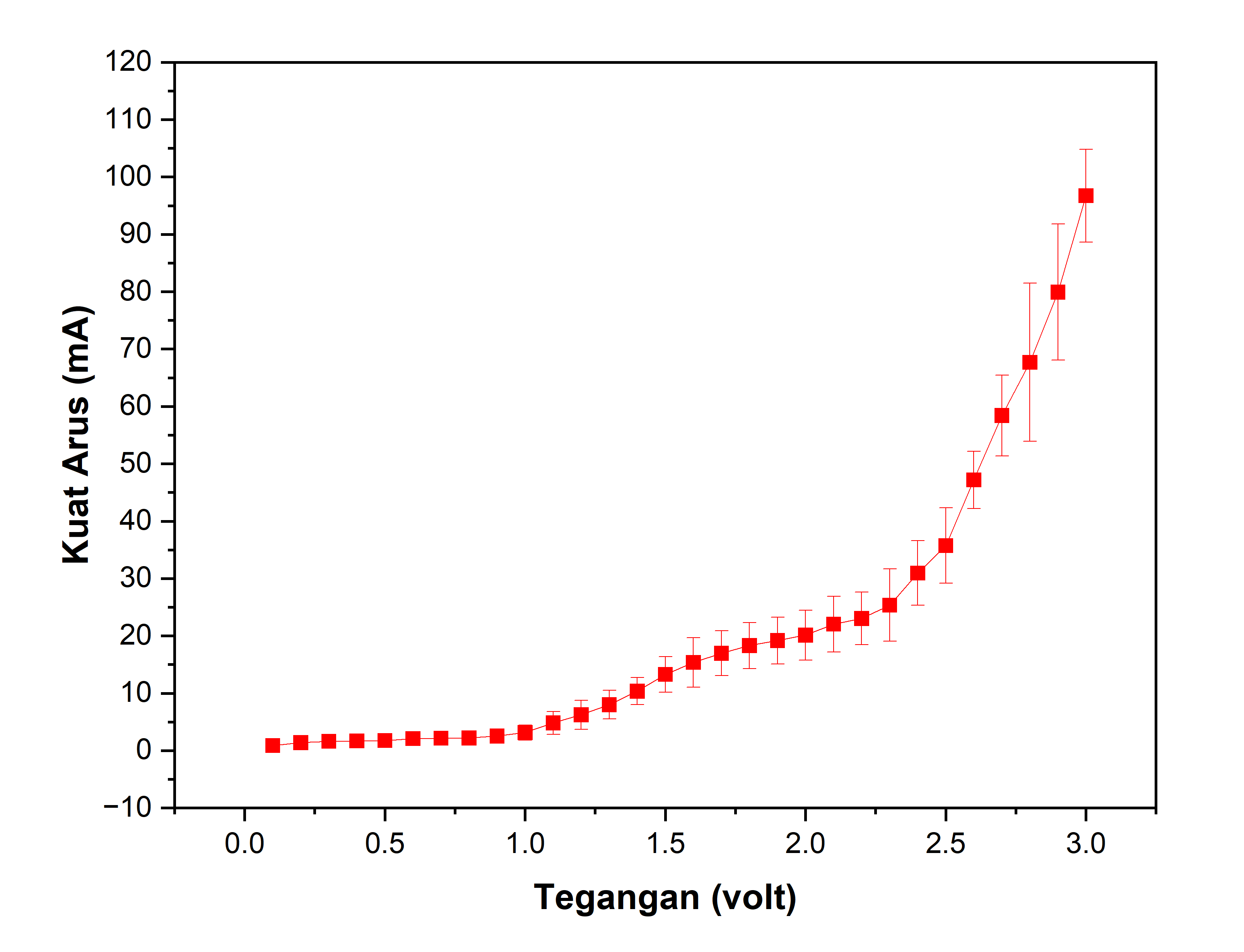
This study investigates the effects of temperature and electric current on the aluminum (Al) elektroplating process onto copper (Cu) substrates using nickel- (Ni) and silver-based (AgNO₃) electrolyte systems under potentiostatic control. The analysis emphasizes current stability, voltage response, and the structural quality of the deposited metal layer on the cathode surface. Elektroplating was performed at two temperature conditions—ambient temperature and 40 °C—with applied potentiostatic currents ranging from 0 to 0.2 A. The nickel electrolyte consisted of NiSO₄, NiCl₂, and H₃BO₃, while AgNO₃ and KCN served as the components of the silver electrolyte. The findings reveal that temperature exerts a significant influence on the deposition rate and uniformity of the coating; elevating the temperature to 40 °C enhances reaction kinetics and yields a smoother and more homogeneous surface. Variations in electric current further affect the thickness and morphological quality of the deposit, where higher current intensities accelerate deposition but may induce surface irregularities. Overall, the potentiostatic technique demonstrated reliable control over the electrochemical deposition process, making it an effective approach for assessing the relationship between electrical parameters and the quality of the resulting metallic coating.